Microsoft Teams Security (2025): How do you make collaboration secure?
Quick overview:
- You will learn how to securely set up external collaboration for guests or external users or with shared channels.
- You will learn how Purview Data Loss Prevention (Purview DLP) prevents data loss.
- You will receive clear steps for meeting protection, roles, and policies.
- You will receive use cases and product solutions such as External User Manager (EUM) and Teams Manager.
In this first part of our blog series, we will dive into Microsoft Teams Security details related to collaboration aspects. Part 2 takes a deeper look at configuring compliance settings for Microsoft Teams, while part 3 covers the specific settings for security in Microsoft Teams.
Collaboration aspects of Microsoft Teams Security
Please note that while all these collaboration settings make your MS Teams environment safer, they may impede the collaboration between users.
What is “secure collaboration” in Microsoft Teams today?
Secure collaboration means control over who, what, and how content is shared, plus protection of sensitive data in chats, channels, and meetings.
Essential components:
- Microsoft Entra ID / Cross-Tenant Access: Identity and access control.
- Guest access, external user access, shared channels: each for a different scenario.
- Microsoft Purview DLP: Policies for data loss prevention in chats, channels, files. Here is a related article in Microsoft Learn: Data Loss Prevention and Microsoft Teams.
- Teams meeting protection: e.g., watermarks, end-to-end encryption.
- Governance & product solutions such as External User Manager & Teams Manager for automation, reporting, lifecycles.
Who does this apply to in particular?
IT administrators, compliance officers, security officers in organizations with external partners or multiple tenants.
What is the difference between external access, guest access, and shared channels?
| Option | Scenario | Access & Restriction | Control via settings |
| External access | External domains should be allowed to chat/call, but not receive team or file shares | Chat/calls only, no team membership | Teams Admin Center -> External Access; Domain Allow/Block Lists |
| Guest access | External collaborators need access to channels, files, boards, etc. within a team. | Full access to team channels and files; restrictions possible via guest roles. | Teams Admin Center -> Guest access + Entra External Collaboration Settings |
| Shared Channels (with B2B Direct Connect) | External users collaborate only in specific channels without full team membership, avoiding tenant switching | Channel access only, no access to the entire team; users are distributed according to tenant | Entra External Identities -> Cross-tenant Access Settings, Shared Channels Policy in Teams Admin Center |
How do I control external collaboration via Entra Cross-Tenant Access?
Short answer: Enable cross-tenant settings inbound & outbound, define domains & applications, manage policies with least privilege.
Steps for implementation:
- In Microsoft Entra Admin Center -> External Identities -> Cross-tenant access settings -> add domain or tenant. Article in Microsoft Learn: Collaborate with external participants in shared channels
- Configure inbound and outbound settings: Allow users/groups, applications.
- Enable Shared Channels Policy in the Teams Admin Center: specify who can create shared channels and who can be invited externally.
- Control domain lists (allow/block), MFA/device compliance, sensitivity labels, etc.
- Monitoring & reporting: Check logs for cross-tenant activities, define alerts.
The simple solution:
With External User Manager for M365 guest management, you can automate guest lifecycles, centrally allow or block domains, and view reports on guest usage. Get a free demo here.
How do I manage Teams meeting settings? – Permissions and policies
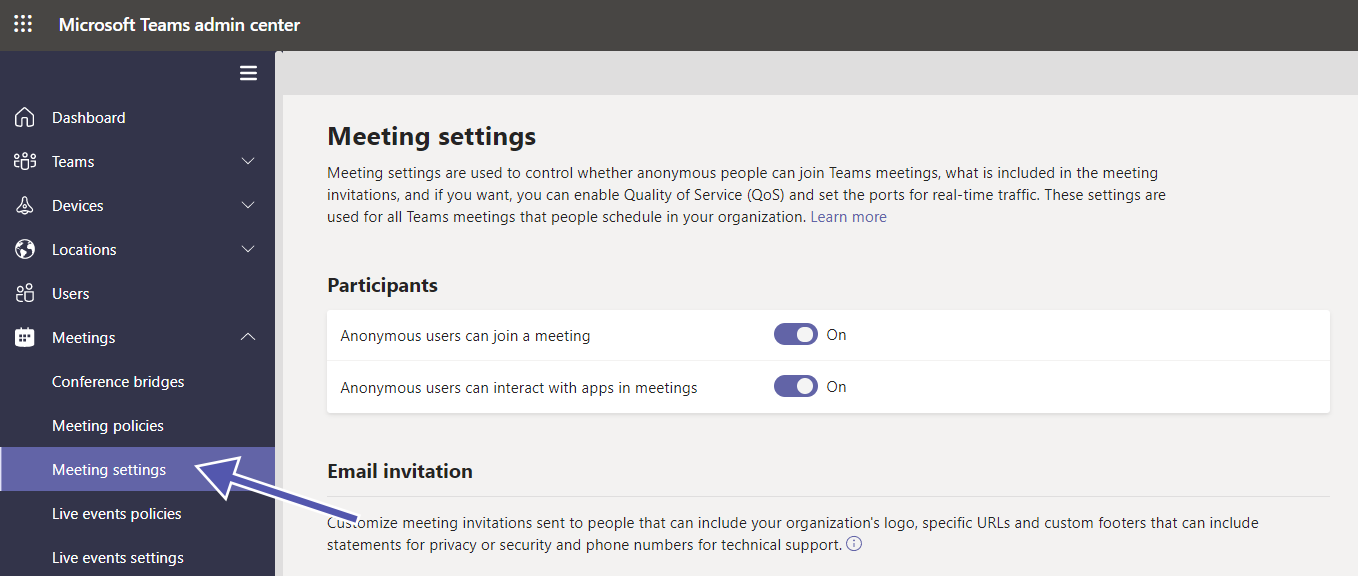
In the Teams Admin Center (https://admin.teams.microsoft.com) you can change meeting seetings for individual participants’ permissions. These can be applied either as an organization-wide default or for specific meetings. This is especially relevant for “meet now” meetings.
Change the settings on
- getting notifications for participants who join or leave the meeting
- participants who can skip the waiting area
- presenter permissions in the meeting
- muting attendees (and not enabling them to unmute themselves)
There are numerous options to adapt your organization-wide meeting settings and meeting policies which would go beyond the scope of one single (or three) blog articles. For more information, check out these very detailed articles by Microsoft here, here and here.
How can I designate roles for meetings in Microsoft Teams?
Here we will discuss temporary designations you can give to the participants of a meeting. It gives a secure and reliable meeting experience. How you can designate participants and how to set up policies is explained below.
What roles in a Microsoft Teams meeting are there?
When you organize a meeting where multiple people will attend, you can assign different roles to the participants with different options to contribute to the meeting. The roles are classified into three groups: organizers, presenters, and attendees.
Organizers and presenters have access over all features, while attendees have a more limited role.
Organizers and presenters have control over sharing videos. They can communicate through chat or voice, remove any participant, admit users from the lobby, start and stop live transmission or recording, mute other users, get control over other participant’s presentations, etc.
The attendees’ role is limited to sharing a video, participating in the communication, and privately viewing a presentation file shared by someone else.
Changing meeting roles
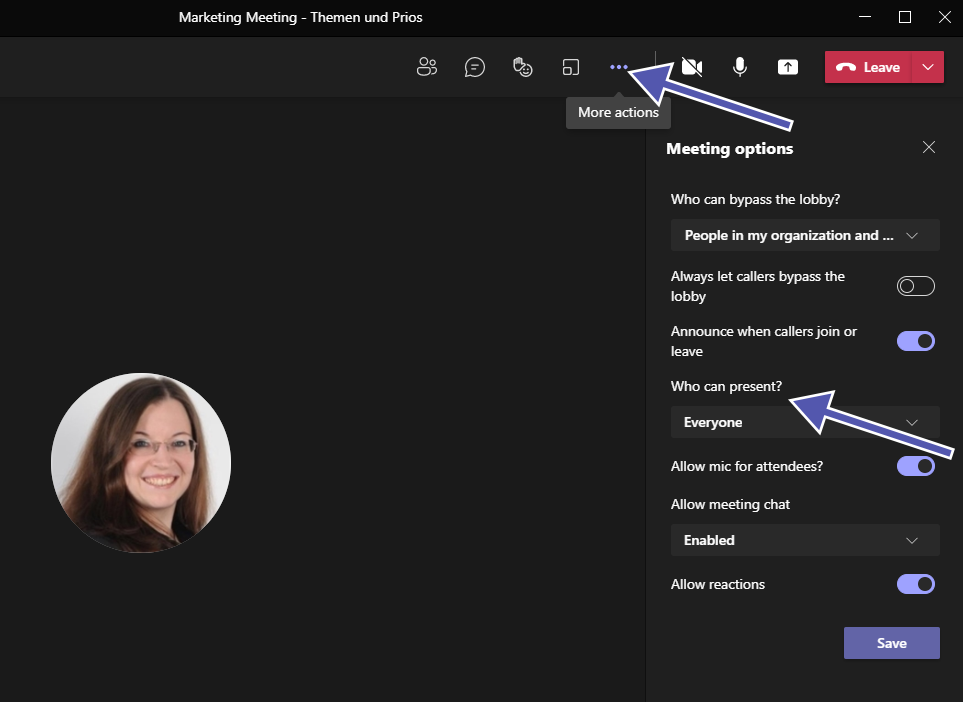
Before assigning the roles to the meeting participants, you need to send out the invitations to the meeting. After sending the invites, go to your calendar and select the meeting you have created. Then go to the Meeting Options, which will open a new page.
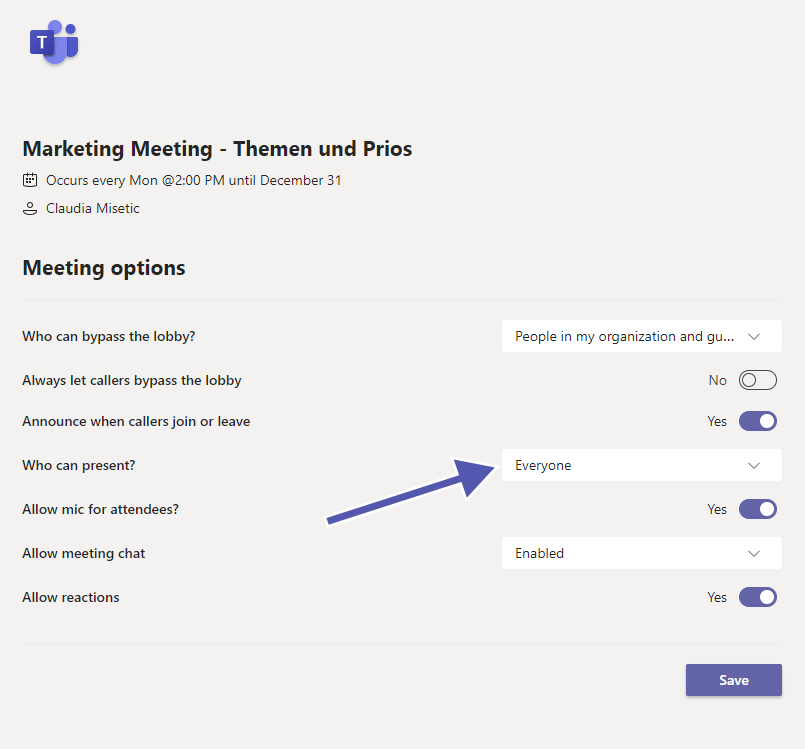
Here you can see several options under the dropdown menu “Who can present?” and are able to update the designated roles of the participants accordingly.
Please note: You need to send an invite directly to the people you want to choose as a presenter. Also, you can’t select a participant from a different organization as a presenter.
Changing roles during a meeting
There are also two ways to change participants’s roles when you are in the middle of a meeting:
- Go to the calendar, select the meeting, then click on “meeting options”. Open the dropdown menu at “Who can present?” to add a new presenter. (see point 5.2 for details)
- Select “Show participants” in the meeting controls to get the list of all the meeting participants. Hover over the user’s name whose role you want to change, then select “More options.” Now you can select either “Make an attendee” or “Make a presenter.”
What do I need to know about Cloud Recordings?
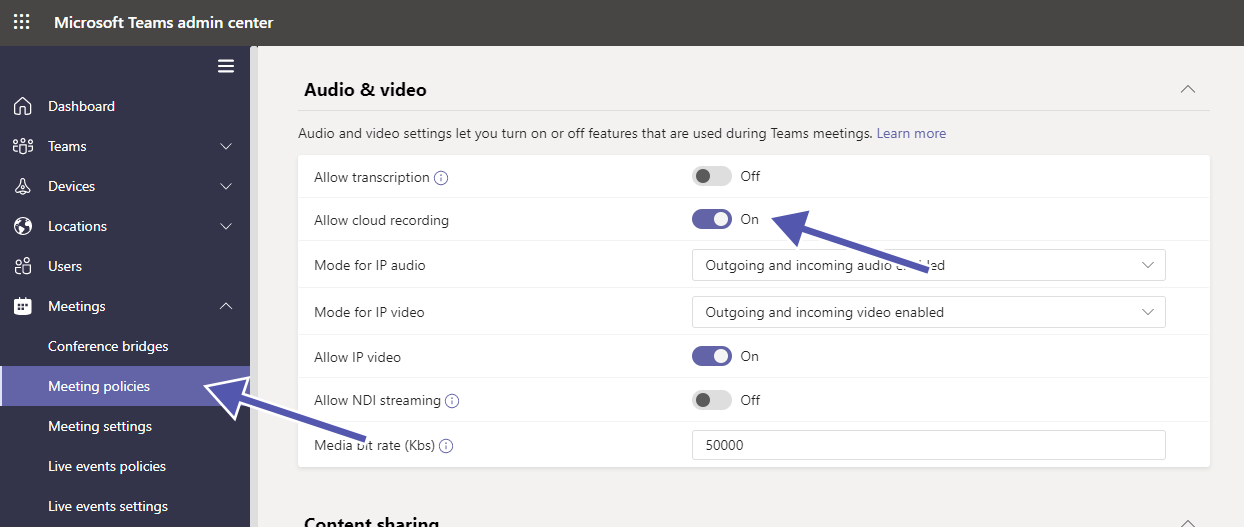
Recording meetings is an excellent feature that Microsoft Teams offers, but you should make sure to know where the data and videos are stored. Also it is critical to understand compliance and get the participants’ consent prior to recording the videos (which Teams now does automatically).
How do you implement meeting protection (watermarks, E2EE, roles)?
In short: If meetings are confidential, use Teams features such as watermarks and end-to-end encryption (E2EE). Also, define roles and meeting policies.
Step-by-step implementation:
- Check whether your tenant is licensed for the relevant features.
- Introduce sensitivity labels with meeting labels: automatic or recommended application.
- Create meeting policies: use the lobby, restrict screen sharing, specify who can use chat/file sharing.
- Enable watermarks for sensitive meetings.
- Use E2EE (end-to-end encryption) for 1:1 or small group meetings, if necessary.
How can I activate Teams Channel Moderation?
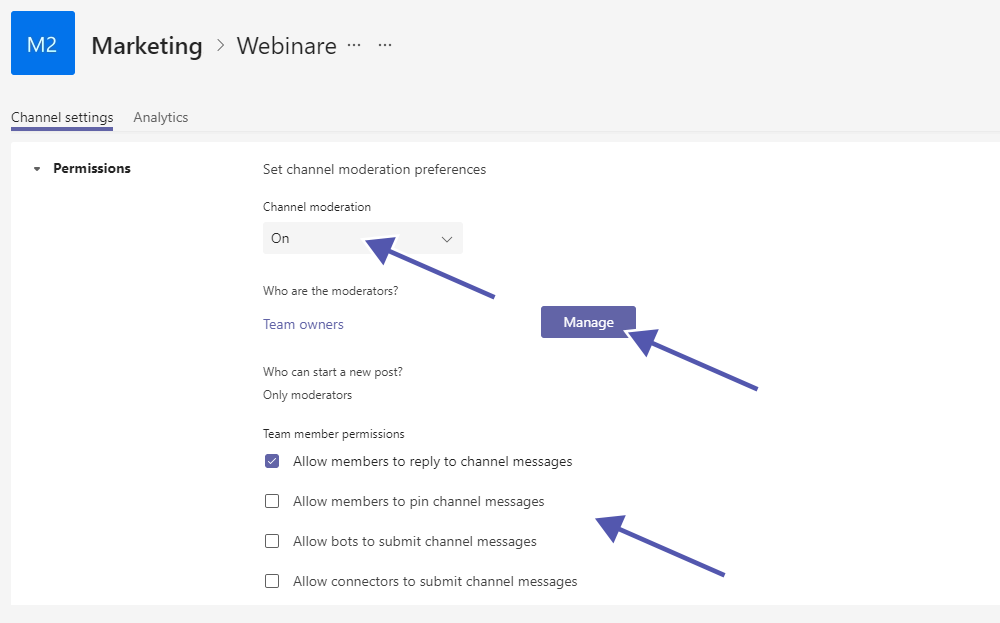
With activated channel moderation, team owners have control over who can perform specific tasks in specific channels. You can find these settings by clicking on the three dots next to the channel’s name and selecting “Manage channel”.
For example, the “General” channel can be used only for announcements this way, which may be especially helpful in project teams with external guest users. Another way to use channel moderation is to allow only discussions on a specific topic: The team owner can start a post, and the team members can answer and discuss it in the answers.
If you activate the channel moderation in Microsoft Teams, a moderator can perform the following tasks.
- Only the moderator can start new posts on the channel.
- The moderator can add or remove other team members as moderators. The team owner, however, is always set as moderator and can’t be removed.
- The moderator can decide whether team members are allowed to pin channel messages.
- The moderator can decide whether to allow team members to reply to channel messages.
- The moderator can decide whether connectors and/or bots can submit channel messages.
What are Microsoft Teams Apps Permissions?
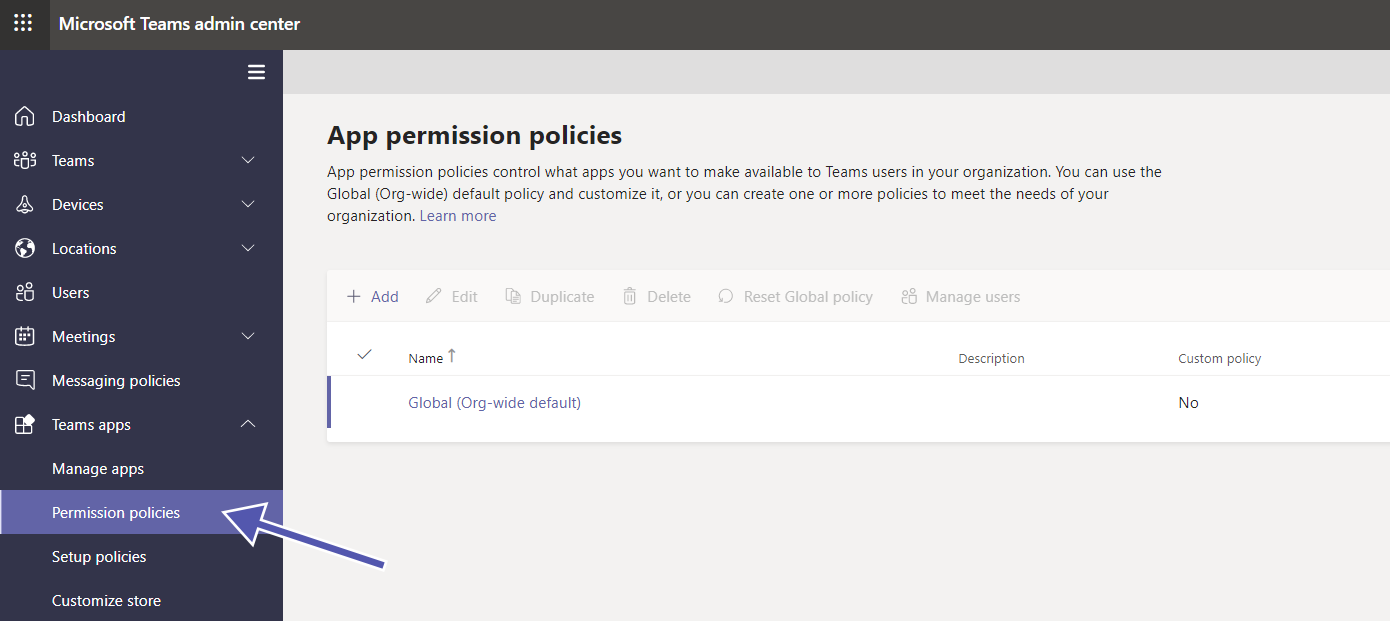
Using this setting, you can manage your organization’s Microsoft Teams apps in the Teams Admin Center. Admins can change security settings for apps, app setup policies, permission policies, etc. With these settings, admins can control the use of apps in their organization and create a better, more secure collaboration environment.
These are the available options:
- You can set a global org-wide policy to define what apps are available throughout the organization.
- You can create individual app permission policies to define what apps are available for specific teams or specific users.
- You can also pin the users’ critical apps to make it more convenient for them to find those.
Read this blogpost for more details on the setting options for Microsoft Teams app permission policies.
What can I control with org-wide settings for Microsoft Teams?
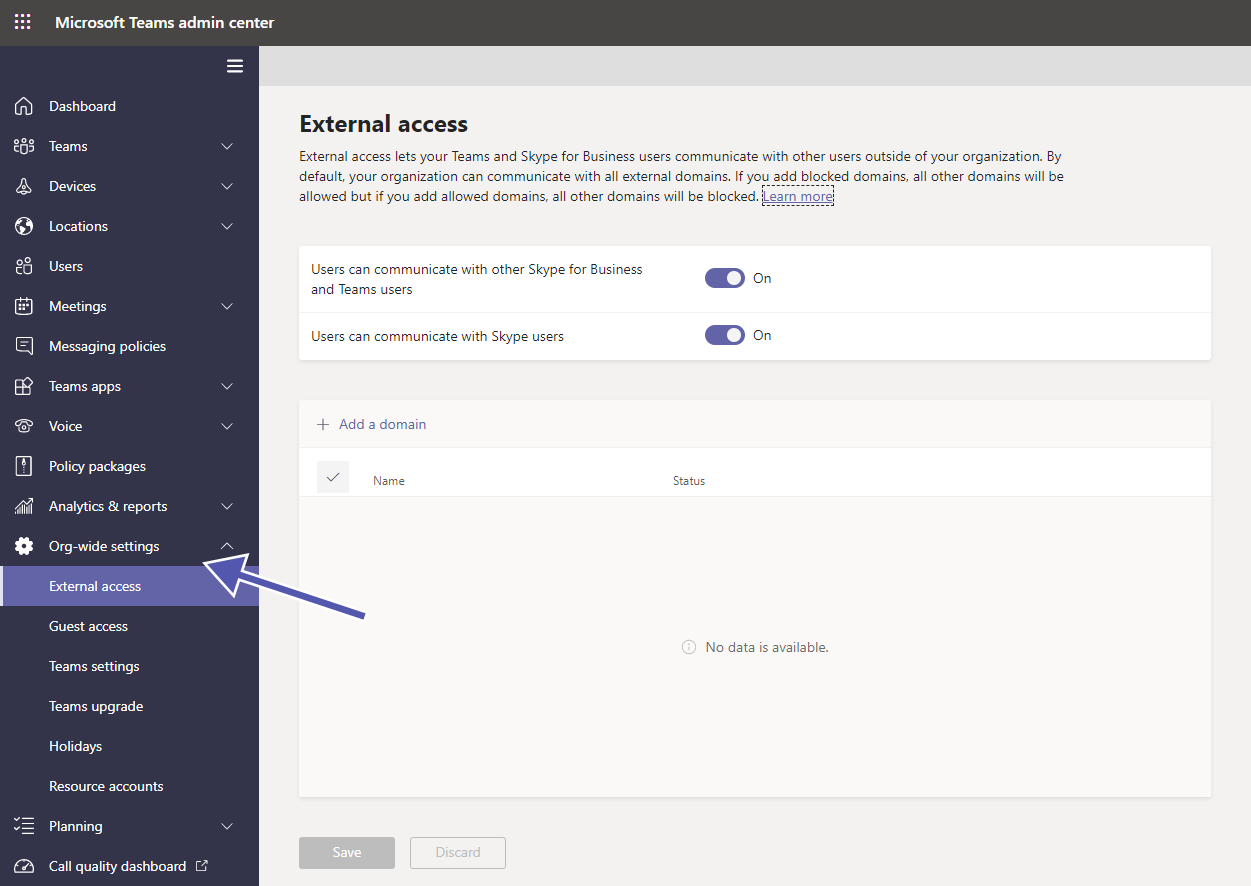
In the Teams Admin Center you can find a variety of org-wide settings to control which users may access your environment and your data.
There are two kinds of settings for people from outside your organization: guest access and external access. You can find even more details in this blogpost on how to control your guest access settings.
How can I start with implementation of guest access?
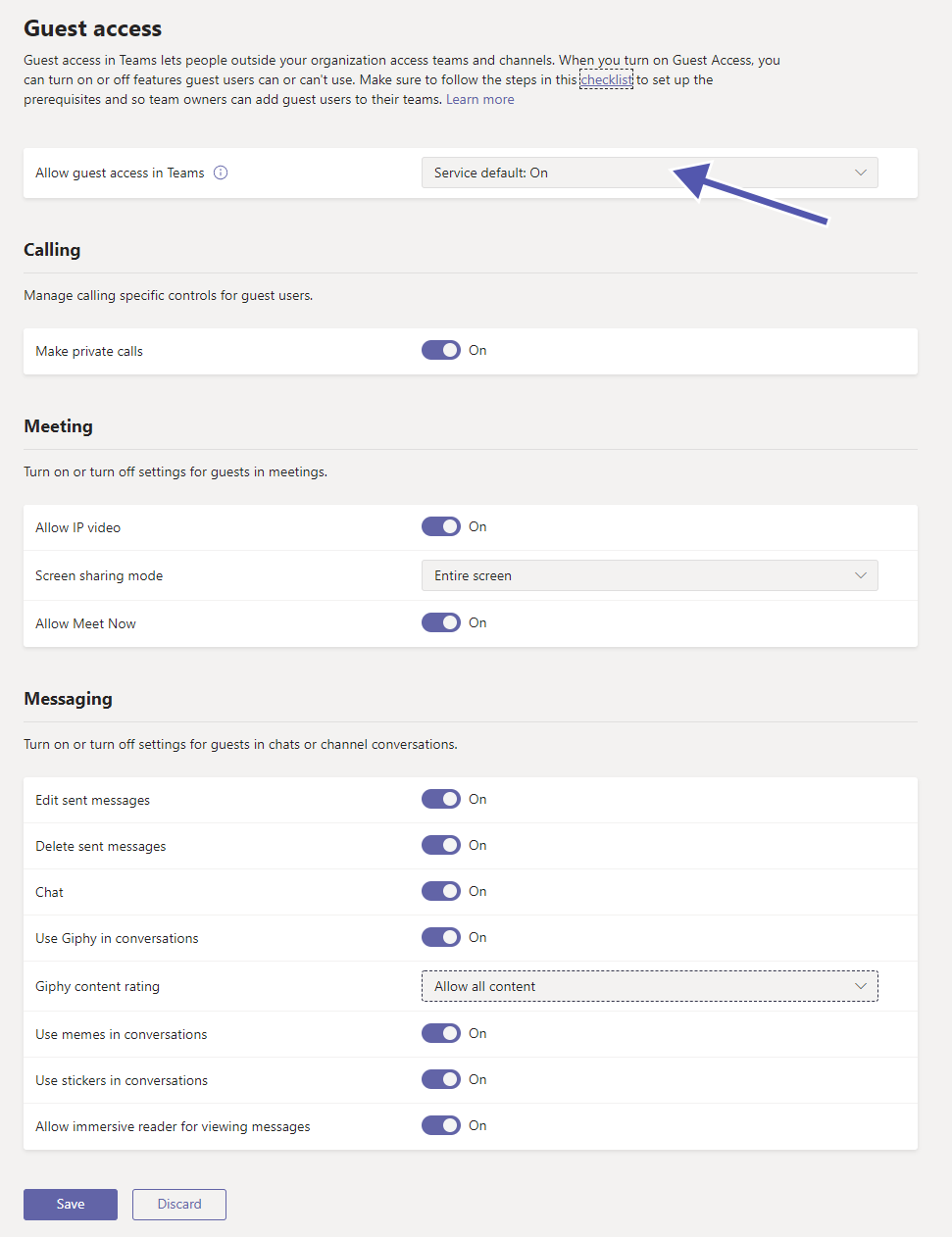
Guest users have almost the same level of access like team members. It is critical to understand how it is different from external access. Microsoft Teams has enabled the guest access feature by default.
Activate or deactivate the following options for guest users:
- Allow or deny guest access in Teams overall (the default is set to “on”)
- Make private calls
- Allow IP video
- Screen sharing mode
- Allow Meet Now
- Edit sent messages
- Delete sent messages
- Chat
- Use Giphy in conversations
- Giphy content rating
- Use memes in conversations
- Use stickers in conversations
- Allow immersive reader for viewing messages
Manage guest users in Microsoft Teams with External User Manager. Use approval workflow, access control, reporting and more.

And how can I start with implementation of external access?
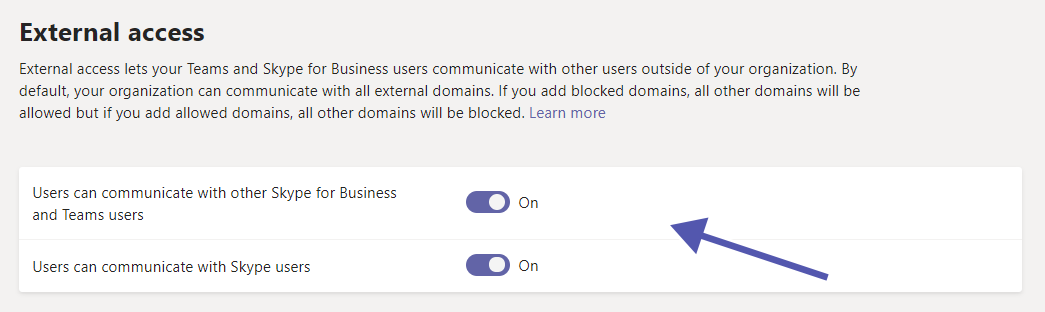
External access is enabled by default when Teams is deployed. However, administrators can of course decide to deactivate it instead.
If you decide to leave external access enabled, you have several options to control the level of access. For example, you can allow or block any domain. You can also define whether users should be able to communicate with other Teams users.
The main reason for disabling external access is to only give access where it is really required. Of course this means more effort on part of the IT and admins, but the higher level of security more than makes up for it.
How can I secure data with information barriers?
With Information Barrier policies you can prevent groups and individual users from communicating between each other. This is an important component for keeping data and information secure in your organization.
You can either restrict a team from communicating with one other, specific team, or restrict a team from communicating with any other team.
Usually, information barriers occur when any of the following take place.
- A new member is added to the team.
- A new participant is invited to join a meeting.
- A user makes a phone call (VOIP call) in Microsoft Teams.
- A user shares a screen.
- A user requests a new chat.
- Whenever there are guest users in Teams.
How do I prevent data loss in chats and channels with Purview DLP?
The short answer: Set up Purview DLP policies (Data Loss Prevention policies) that cover chats, channel messages, and private channels; start with default policies and refine them further using classification and sensitivity labels.
Instructions:
- Check your license status (e.g., Microsoft 365 E5 or comparable required). Here is an article in Microsoft Learn about data loss prevention and Microsoft Teams.
- Create a DLP policy in the Purview portal -> Select locations: Teams Chat & Channel Messages (standard and shared).
- Define sensitive information types (e.g., credit card numbers, personal data, financial data).
- Enable policy tips: Users see notifications before sharing data.
- Test run & monitoring: Configure alerts, document incidents.
How do I prevent sprawl of teams, channels, and permissions?
Simply put: Standardize through templates, naming conventions, and lifecycle processes; control permissions and guest access.
Implementation plan:
- Define naming conventions for teams, channels, and shared channels.
- Create templates (e.g., a standard template for each department) via Teams Manager.
- Roles & policies: who is allowed to create teams, who is allowed to invite external users.
- Periodic review of guests & members (e.g., every 3-6 months).
- Reporting: audit logs (guest activities, newly created teams or channels, policy compliance).
The solution:
Teams Manager takes care of templates, lifecycles, and naming conventions; External User Manager specifically handles guest lifecycles and access reviews.
Get a demo here:
Checklist: Which 10 collaboration settings should you check today?
- Cross-tenant access (inbound & outbound) for partner tenants.
- Shared channel policies enabled.
- Guest access policy defined.
- External access domain allow & block configuration.
- Purview DLP policy with coverage for chats & channels.
- Sensitivity labels for meetings/artifacts.
- Meeting protection policies: lobby, chat, screen sharing.
- Naming convention & templates in place.
- Regular review of guests/teams through lifecycles.
- Reporting & monitoring set up: logs, audit, security alerts.
FAQ: The most frequently asked questions in practice
Get started with Purview DLP: Enable default policy -> include all chats & channels -> define sensitive information types -> enable policy tips.
When external employees should only work in certain channels and full access is not desired. Shared channels with B2B Direct Connect ensure that users no longer have to switch tenants.
Via Entra “External collaboration settings” and Teams Admin Center -> Guest Access Settings. Then use the domain lists, groups, and roles.
Use sensitivity labels, defined meeting roles, and watermarks. Activate the lobby rule.
Through Teams templates, naming conventions, and restricting who can create Teams/channels. Archive unused Teams using lifecycle processes.
With automated access reviews (e.g., every 3–6 months) with External User Manager.
Next steps for greater security when collaborating in Microsoft Teams
Request a demo of External User Manager: See guest lifecycles and domain control live.
Request a demo of Teams Manager: Automate templates, naming conventions, and governance.
This covers the Microsoft Teams security settings related to aspects of Collaboration. For a look at configuring compliance settings for Microsoft Teams, see part 2 of our blog series, while part 3 covers settings specific to security in Microsoft Teams.


CEO and Governance Expert at Solutions2Share
Christian Groß is a Microsoft Teams governance expert from the very beginning. Over the past 6 years, he has developed 6 Teams apps, founded Solutions2Share, and launched the German-speaking Microsoft 365 conference in Mainz, Germany.
He regularly speaks at international M365 events and supports IT leaders in building scalable governance strategies.